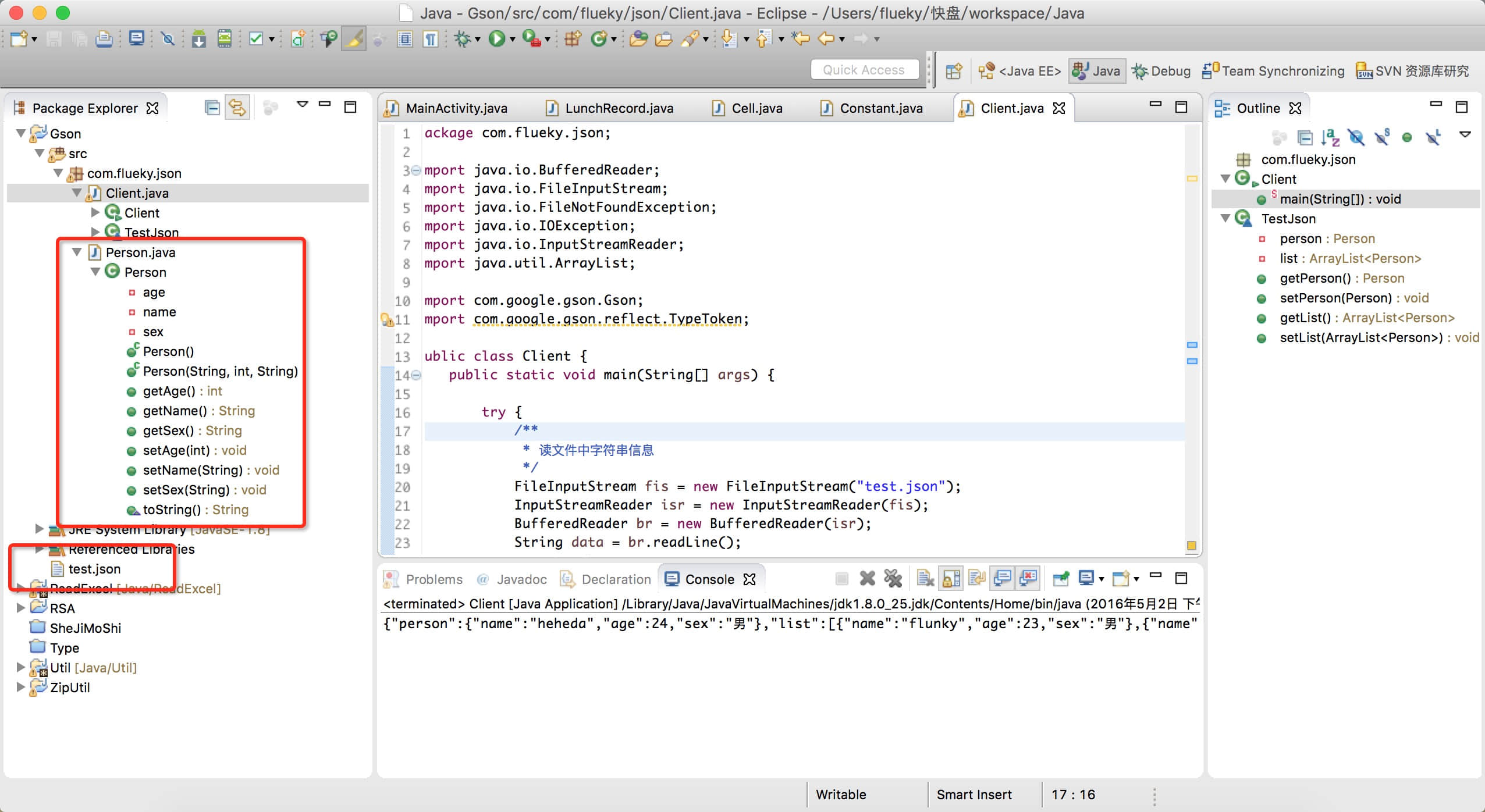
JSON(JavaScript Object Notation) 是一种轻量级的数据交换格式。它基于ECMAScript的一个子集。 JSON采用完全独立于语言的文本格式,但是也使用了类似于C语言家族的习惯(包括C、C++、C#、Java、JavaScript、Perl、Python等)。这些特性使JSON成为理想的数据交换语言。 易于人阅读和编写,同时也易于机器解析和生成(一般用于提升网络传输速率)。
基础结构
对象结构
1
2
3
4
5
| {
"name":"flunky",
"age":23,
"sex":"男"
}
|
数组结构
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| [
{
"name":"flunky",
"age":23,
"sex":"男"
},
{
"name":"heheda",
"age":24,
"sex":"男"
}
]
|
JSON的结构只有以上两种,而在实际应用中,见到的通常是以下的混合结构
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| {
"list":[
{
"name":"flunky",
"age":23,
"sex":"男"
},
{
"name":"heheda",
"age":24,
"sex":"男"
}
],
"person":{
"name":"heheda",
"age":24,
"sex":"男"
}
}
|
推荐在线JSON解析工具,运行截图如下:
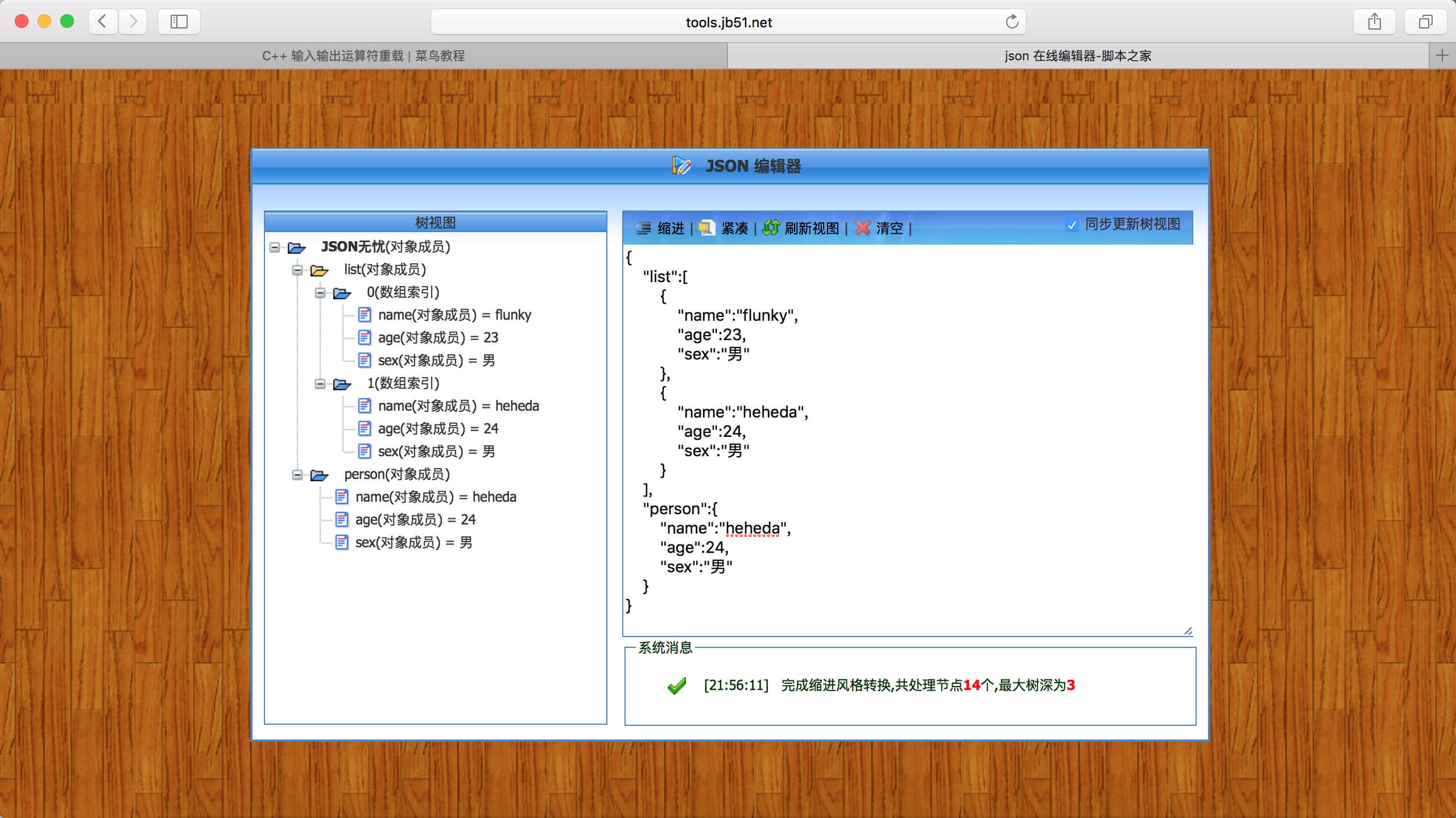
解析json
用Java解析json,主流的两个Jar包分别是Google的Gson(下载点我) 和阿里的FastJson。此处采用Gson解析。
定义好需要解析的实体类。注意每个成员变量名的定义一定要和JSON数据里键值对的键名一致。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
| package com.flueky.json;
public class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
private String sex;
public Person() {
super();
}
public Person(String name, int age, String sex) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.sex = sex;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return name +" "+age+" "+sex;
}
}
|
解析对象格式:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
| package com.flueky.json;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import com.google.gson.Gson;
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("test.json");
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(fis);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(isr);
String data = br.readLine();
br.close();
isr.close();
fis.close();
Gson gson = new Gson();
Person person = gson.fromJson(data, Person.class);
System.out.println(person);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
|
test.json文件内容:{“name”:”heheda”,”age”:24,”sex”:”男”}
解析数组格式:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
| package com.flueky.json;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import com.google.gson.Gson;
import com.google.gson.reflect.TypeToken;
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("test.json");
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(fis);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(isr);
String data = br.readLine();
br.close();
isr.close();
fis.close();
Gson gson = new Gson();
ArrayList<Person> persons = gson.fromJson(data, new TypeToken<ArrayList<Person>>() {
}.getType());
for (Person p : persons) {
System.out.println(p);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
|
test.json文件内容:[{“name”:”flunky”,”age”:24,”sex”:”男”},{“name”:”heheda”,”age”:23,”sex”:”男”}]
解析混合格式:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
| package com.flueky.json;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import com.google.gson.Gson;
import com.google.gson.reflect.TypeToken;
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("test.json");
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(fis);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(isr);
String data = br.readLine();
br.close();
isr.close();
fis.close();
Gson gson = new Gson();
TestJson testJson = gson.fromJson(data, TestJson.class);
String jsonData = gson.toJson(testJson);
System.out.println(jsonData);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
class TestJson {
private Person person;
private ArrayList<Person> list;
public Person getPerson() {
return person;
}
public void setPerson(Person person) {
this.person = person;
}
public ArrayList<Person> getList() {
return list;
}
public void setList(ArrayList<Person> list) {
this.list = list;
}
}
|
test.json文件内容:{“list”:[{“name”:”flunky”,”age”:23,”sex”:”男”},{“name”:”heheda”,”age”:24,”sex”:”男”}],”person”:{“name”:”heheda”,”age”:24,”sex”:”男”}}
最后附上Java工程目录截图